Appearance
iChannel0–iChannel3
The iChannel uniforms allow you to pass external textures into your shader. These are typically image samplers used for lookup, masking, layering, or stylized effects.
You can access up to four channels in your shader:iChannel0, iChannel1, iChannel2, and iChannel3.
In WGSL, textures and samplers are defined separately:
iChannelN:texture_2d<f32>iChannelNSampler:sampler
WGSL separates the texture (texture_2d<f32>) and sampler (sampler)
Textures are sampled using normalized UV coordinates: vec2<f32> in the [0.0, 1.0] range.
Images are managed in the UI via the Texture Panel, where you can upload or assign textures per channel.
Usage
Each channel is made up of two parts:
- A 2D float texture:
texture_2d<f32>(e.g.,iChannel0) - A sampler:
sampler(e.g.,iChannel0Sampler)
To read from a texture, both the texture and its sampler must be passed to textureSample.
Common Use Cases
- Read a color from a texturewgsl
let color = textureSample(iChannel0, iChannel0Sampler, uv); - Use a texture as a maskwgsl
let mask = textureSample(iChannel1, iChannel1Sampler, uv).r; - Distort based on another texturewgsl
let offset = textureSample(iChannel2, iChannel2Sampler, uv).rg;
Examples
All the example previews below assume the default textures uploaded in all four channels.
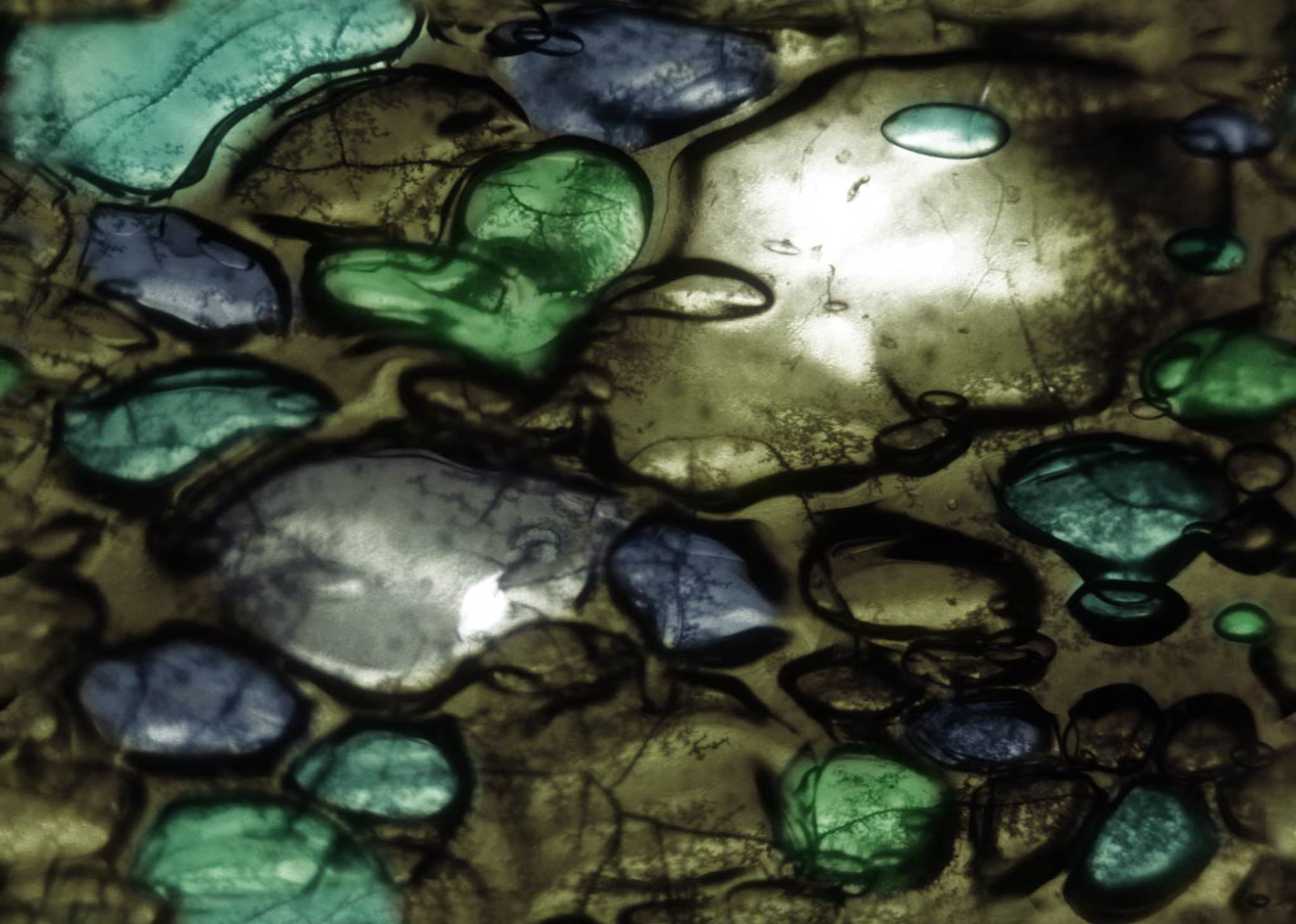
Display a Texture
wgsl
@fragment
fn main(@builtin(position) pos: vec4<f32>) -> @location(0) vec4<f32> {
let uv = pos.xy / iResolution.xy;
return textureSample(iChannel0, iChannel0Sampler, uv);
}This example simply maps the iChannel0 texture directly to the screen using UV coordinates derived from iResolution.
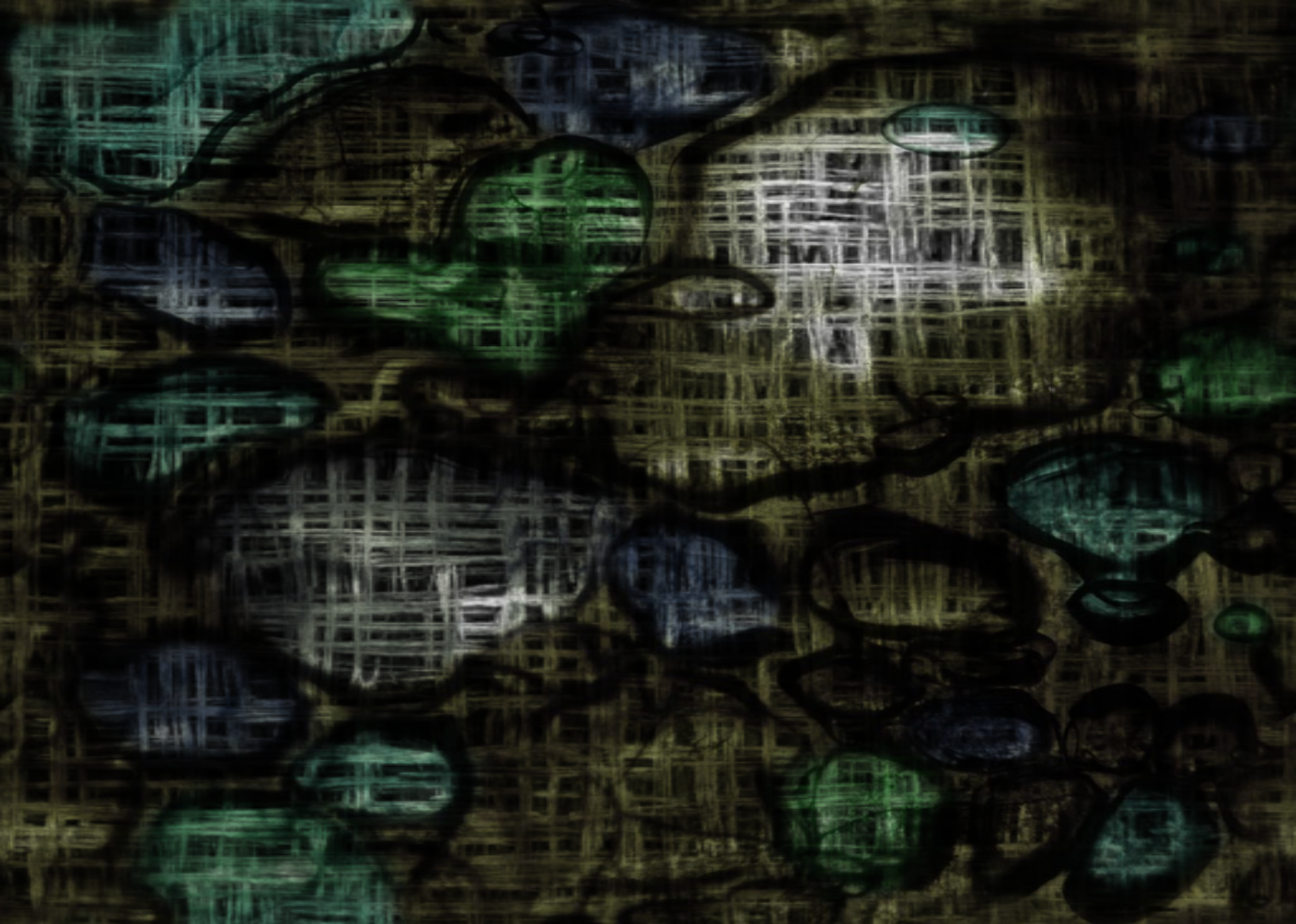
Masked Glow Using Second Texture
wgsl
@fragment
fn main(@builtin(position) pos: vec4<f32>) -> @location(0) vec4<f32> {
let uv = pos.xy / iResolution.xy;
let base = textureSample(iChannel0, iChannel0Sampler, uv);
let mask = textureSample(iChannel1, iChannel1Sampler, uv).r;
return vec4(base.rgb * mask, 1.0);
}This example multiplies the base texture (iChannel0) by the red channel of a mask texture (iChannel1) to create a glowing masked effect.
Looking for a general overview of textures? See What are Textures.
Want to learn how to assign textures in the Splitshade interface? See Texture Usage.